Security Awareness Campaigns And Zero Trust
Security Awareness Programs: IT Security Starts with the Users." we discussed that the users need to feel involved with the awareness programs in...
The major strategic goal of cyber security in the digital age is to combat and mitigate data breaches. A company's data is its most valuable asset to protect. This blog post will explain to you the components of a Zero Trust Model.
↑ Listen to the blog article
Zero Trust Model is a cybersecurity model which maintains strict access control for any user or device. It works by verifying and authorising every connection they make. Conventional security approaches often focus on external threats and its perimeters, leaving the organisation defenceless against insider threat.
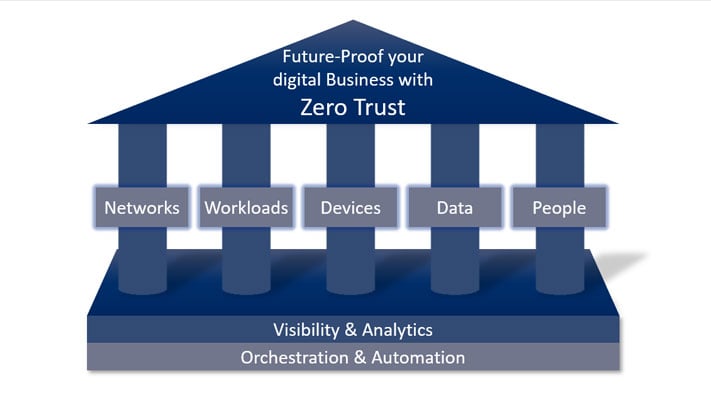
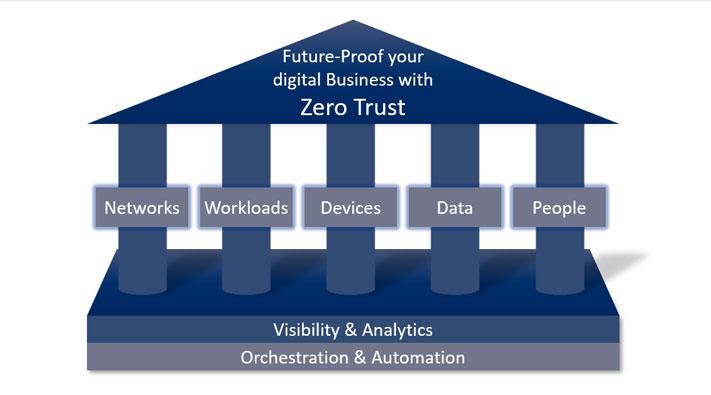
The Zero Trust model is based on the principle "never trust, always verify". No distinction is made between outside and inside. It is also known as Zero Trust Architecture, or just as a ZTA. Zero Trust, therefore, treats all devices, services and users with the same caution. This emphasises the focus on data and gathers security functions into a unified data protection strategy. You are now able to develop a strong defence and detection system with incident response capabilities to protect your business’ critical data.
This model is different from traditional ideas. It takes an equal approach to all devices, services, and users. It also assumes that they cannot be trusted. This is a significant change, known as a paradigm shift.
Find out more how to implement with Zero Trust Security Architecture with 3 easy steps !
The ability to segment, isolate, and control the network remains an important success factor for Zero Trust Model. It must be ensured that only certain units (users, applications or devices) with specific requirements may access sensitive network segments or micro perimeters.
The workload is a generic term that refers to the entire application stack, which is the sum of all applications. In the broadest sense, it is about monitoring applications and their controlled execution across the enterprise network and in the cloud. As with any other area of zero trust, these connections, applications, and components must be treated as a potential attack vector and equipped with zero-trust control mechanisms and technologies.
IoT and network-based device technologies have created enormous potential for network and enterprise endangerment. Security professionals must take steps to implement a zero-trust strategy. This requires the ability to isolate, secure and control every device and computer on the network at all times.
One of the pillars of a zero-trust strategy is data security. The key components of this approach are for example: securing and managing data, categorising and developing data classification schemes.
Companies must also consider the user in the zero trust strategy so that they do not become the gateway to attacks. Most companies today do not know how much power and trust they give users. The authority of any strategy is to restrict user access. This includes securing login and protecting users while interacting with the company network.
This includes all the technologies required to authenticate users (e.g. multi-factor authentication) and continuous monitoring and controlling of their access and permissions.
“Users, employees, business partners and even customers often do not know what role their actions play in a holistic security strategy.“
Read more on IT Security and find out what is crucial to strenghten it:
Visibility is the key factor in defending valuable assets of the business, e.g. data, knowledge, or corporate secrets. But you cannot protect the invisible and you cannot fight a threat that you do not see or understand.
Zero Trust Model requires security teams to maintain visibility and control over their entire digital business environment, regardless of location, device, user count, or hosting model.
Tools such as security information management (SIM) systems or advanced security analytics platforms, security user behavioural analytics (SUBA) and other analytic systems, provide visibility into user activity on the network and the endpoints.
Try DriveLocks Solution to protect your sensitive data for 30 days and strenghten the Zero Trust Model in your company.
A zero trust platform uses technologies that enable automation and orchestration.
Analytics demonstrate the value of automation and orchestration tools and technologies for businesses and security teams. These tools and technologies enable companies and security teams to streamline their operations across the enterprise. It must be possible for leading providers of these platforms to be able to integrate into other systems to use complementary security information or pass on useful data. Conversely, companies must be able to automate their business processes.
Adopting a zero trust model yields significant advantages in bolstering an organization's security resilience. By consistently validating every access attempt, the risk of unauthorized entry and subsequent data breaches is substantially reduced.
This approach inherently shrinks the attack surface, as no user or system operates under a blanket of trust, limiting the pathways an adversary can exploit. Furthermore, the granular visibility and control afforded by a zero trust model, where every action is authenticated and often logged, enables faster detection of suspicious activities and more effective incident response.
Even in the event of a successful intrusion, the principle of least privilege and network segmentation inherent in a zero trust model curtails lateral movement, minimizing the potential for widespread damage. These security enhancements, coupled with the model's adaptability to remote work and cloud environments, make the zero trust model a cornerstone of modern security strategies.
While the benefits of a zero trust strategy are compelling, its implementation is not without hurdles. Organizations embarking on this journey should be aware of several key challenges:
Complexity of Implementation: Shifting from traditional perimeter-based security to a zero trust strategy often requires significant architectural changes, impacting existing infrastructure and workflows. Integrating new security tools and ensuring interoperability can be intricate.
Performance Overhead: The continuous verification and authentication processes inherent in a zero trust strategy can introduce some latency if not implemented efficiently. Optimizing these processes to minimize impact on user experience and system performance is crucial.
Organizational Culture Shift: A successful zero trust strategy demands a fundamental change in how users and IT teams approach security. Overcoming ingrained trust assumptions and fostering a security-conscious culture across the organization requires effective communication and training.
Initial Investment Costs: Deploying the necessary technologies and expertise to implement a comprehensive zero trust strategy can involve substantial upfront investment. Justifying these costs and demonstrating the long-term return on investment is important.
Maintaining Consistent Policy Enforcement: Ensuring consistent application of zero trust strategy principles across a diverse and evolving IT environment, including cloud services and remote devices, requires robust policy management and enforcement mechanisms.
DriveLock’s approach involves an integrated solution to implement holistic protection across your entire security architecture. DriveLock brings Zero Trust to the endpoint and enables a comprehensive Zero Trust security strategy:
With Encryption, we ensure that no data will leave in a readable format. In order to prevent the loss of data, DriveLock’s encryption software will monitor applications accessed by your employees. User authentication and authorised individual personnel passwords will be enforced.
You can centrally manage your BitLocker encrypted endpoints from a single management console. This also provides a Compliance Dashboard to view the encryption status of all machines within your organisation.
With DriveLock’s Device Control, only the authorised devices of authorised users are allowed access to company data. DriveLock's Application Control works in a similar manner. It includes whitelisting apps to assess potential risks involved when running the application.
Prevention Technologies are not perfect. If attackers manage to bypass the defense, they can go unnoticed for weeks and months. Our Analytics and Forensics module offers a monitoring system for you to track a security breach. DriveLock details which computer, which user and which app was breached. Automated reports will show you results within minutes of the incident.
DriveLock SmartCard Middleware and Virtual SmartCard support and enforce multi-factor authentication. Passwords are still one of the biggest weaknesses for IT security. Whether it is increasingly due to more realistic fraud and phishing mails or weak Passwords.
Smart SecurityEducation enables individuals in your company to develop their understanding of and guard against potential risks in order to effectively protect themselves and your business from cyber-attacks.
Cybersecurity has become more and more like an arms race. It’s not a matter of if, but when, there will be an incident.
By applying measures of Zero Trust to your organisation, you will benefit from:
The transition to a zero trust strategy represents a fundamental evolution in how organizations approach cybersecurity. By abandoning implicit trust and embracing continuous verification, businesses can construct a far more resilient and adaptive security framework capable of withstanding modern threats.
While the journey may present certain complexities, the enhanced security posture, improved visibility, and reduced risk of significant breaches offered by a zero trust strategy make it an indispensable element of any forward-thinking security roadmap. Embracing the principles of "never trust, always verify" is not merely a security trend; it's a strategic imperative for navigating the intricate and ever-evolving cyber landscape and safeguarding valuable digital assets.
More info? Watch the recording of our webinar "Never trust, always verify! - the DriveLock Zero Trust platform"

Security Awareness Programs: IT Security Starts with the Users." we discussed that the users need to feel involved with the awareness programs in...

Enter the concept of "Zero Trust" in cybersecurity. It's not just a buzzword; it's a paradigm shift. Zero Trust challenges conventional wisdom and...

The threat of malware looms large. From viruses and worms to ransomware and spyware, malicious software poses a significant risk to individuals,...