Security Awareness Programs: IT Security Starts with the Users
Cybersecurity is a hot topic that has penetrated the corners of our society. Regional newspapers regularly write about cyber attacks on local...

Security Awareness Programs: IT Security Starts with the Users." we discussed that the users need to feel involved with the awareness programs in order to be successful. In this post, we look at why passwords can derail a security concept and how the Zero Trust concept can help solve it.
| TABLE OF CONTENT |
In our article "Security Awareness Programs: IT Security Starts with the Users." we discussed that the users need to feel involved with the awareness programs in order to be successful. In this post, we look at why passwords can derail a security concept and how the Zero Trust concept can help solve it.
Despite security awareness, no matter how well taught an employee is, they will still bypass security policies if their productivity is affected. In many cases, the introduction of new security measures fails not because the workforce does not understand the risks, but because the process, technology, or both, are too cumbersome. As a result, users prefer to look for ways to overcome technical limitations and risk choosing their own insecure path.
In the worst case, this results in shadow IT - employees spend valuable time searching for workarounds and increase the risk of exposing or losing sensitive data.
Security awareness campaigns are therefore only moderately successful if the technical requirements and processes are not in place.

One of these obstacles is passwords for authentication. Passwords are still widely used to protect digital resources and data. But they are also the cause of many cyberattacks. According to the Cost of a Data Breach Report 2021 by IBM, 20% of data breaches are due to compromised credentials. Individuals unfortunately tend to use weak passwords that are easy to remember.
These "circulate" in large numbers on the dark web after a successful attack: The number of stolen usernames and passwords there increased by 300% from 2018 to 2020.
Once the attacker has captured the credentials, he can move through the company unnoticed.
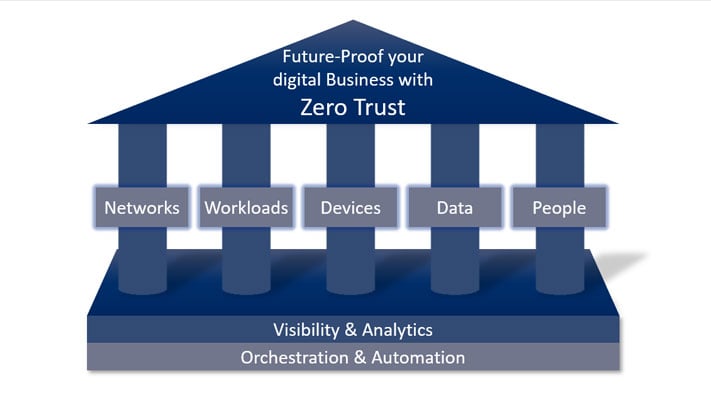
Companies should therefore consider other factors for Identity & Access Management (IAM) and adopt a Zero Trust approach to authentication.
The goal should be to move away from password to passwordless authentication.
The first improvement of password-centric authentication can be the introduction of Single Sign On (SSO) methods. This reduces the frequency of password entry and also the number of passwords required. The shift to remote working (work from home) has led many companies to introduce at least basic Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) with one-time passwords via SMS.
Next step, companies could use another factor in conjunction with passwords consistently for all employees, especially for privileged users and systems, e.g. digital certificates, (hardware or software-based) tokens and access cards. At a minimum, this step could replace SMS-based 2FA with application-based 2FA.
 Authentication without a password is the most advanced, most secure and smoothest level of authentication. Companies use third-party digital certificates or biometric factors. Other factors can be used as an additional security measure, especially for privileged users and systems, more extensive authentication requirements should apply.
Authentication without a password is the most advanced, most secure and smoothest level of authentication. Companies use third-party digital certificates or biometric factors. Other factors can be used as an additional security measure, especially for privileged users and systems, more extensive authentication requirements should apply.
With the "consumerisation of IT" (which began at the latest with the introduction of the iPhone in 2007) and the fact that the digital transformation is making companies more and more permeable, the IT landscape has changed. IT has had to relinquish competencies: Users want the freedom to manage themselves. We work from anywhere, and stakeholders interact with each other along the entire value chain.But if companies want to successfully complete the digital transformation, taking into account the necessary IT security, they have to take the employees with them.Forrester's Zero Trust (ZT) framework describes a modern security architecture for companies. It means moving away from the traditional perimeter-based security approach to a data-driven and identity-aware security model.
Zero Trust not only improves security but has a hidden lever to improve the so-called Employee Experience (EX).
After all, security and productivity are fundamental necessities for modern businesses.What enhances the employee experience?First and foremost, protect the data. Apply the principle of least privilege access. Users should not have more access than they need.Allow employees to work how they want, where they want. Zero Trust allows them to work from anywhere and with any device - as long as they use a properly authenticated compliant device and in a compliant app.
Offer employees choices in technology by using Zero Trust as a principle to verify users, devices and apps before access. Employees who can do this (e.g., bring your own device option) have a higher EX score than those who cannot.Employees in a holistic Zero Trust model don't launch VPN clients, don't have to remember passwords, and don't have to worry about getting their hands on files containing sensitive information not intended for them. Zero Trust solves these problems by authenticating users directly to applications, using passwordless methods, and creating access policies based on the principle of minimal privileges.
Conclusion:
Continue to focus on increasing security awareness, changing behaviour and culture. By making Zero Trust easier for your employees to work with, it becomes easier for them to integrate security into their daily lives, which in turn improves your overall security posture and culture.
Photos: iStock

Cybersecurity is a hot topic that has penetrated the corners of our society. Regional newspapers regularly write about cyber attacks on local...

Imagine this: A cybercriminal doesn't need to be a coding genius to break into your systems. Sometimes, the most potent weapon isn't a complex piece...
The major strategic goal of cyber security in the digital age is to combat and mitigate data breaches. A company's data is its most valuable asset to...