4 Essential Strategies for IT Security
The Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC) is an Australian Government intelligence and security agency who provides advice and assistance on...

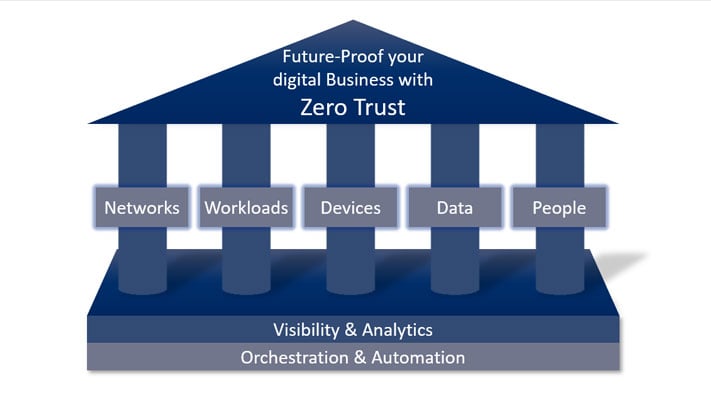
The major strategic objective of cyber security in the digital age is to combat and contain privacy violations. A company's data is its most valuable asset that must be protected. In the last blog post "What elements does a ZERO trust model consist of" we talked about the pillars of a Zero Trust architecture. In this article, we explain step by step how to implement Zero Trust in your company.
| TABLE OF CONTENT |
The assumption of inherent trust in any user, device, or application is a vulnerability modern organizations can no longer afford. The zero trust strategy offers a more resilient security posture by fundamentally shifting this paradigm. Instead of implicit trust, every access request, whether originating inside or outside the traditional network, undergoes rigorous and continuous verification. This "never trust, always verify" approach, underpinned by principles like least privilege and multi-factor authentication, acts as a powerful mechanism to contain breaches and prevent unauthorized access.
This post unpacks the critical advantages a zero trust strategy delivers, outlines actionable steps for its implementation, and illustrates its practical application in safeguarding today's dynamic and distributed environments.
A zero trust strategy is a security framework that assumes no user, device, or system should be trusted by default, whether inside or outside an organization's network. Instead, every access request is continuously verified before granting permissions, using principles such as least privilege, multi-factor authentication, and constant monitoring. This approach minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches by enforcing strict identity verification and
security measures at all points of access, regardless of the user's location or network status.
The zero trust strategy offers several key benefits to companies, enhancing their security and operational resilience. Some of these benefits include:
Enhanced Security: By continuously verifying the identity of users, devices, and applications, zero trust minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. Even if an attacker bypasses perimeter defenses, they face additional authentication barriers.
Reduced Attack Surface: Zero trust strategies ensure that no user or system is automatically trusted, reducing the areas an attacker can exploit. Segmenting networks and restricting access to only what's necessary significantly limits potential vulnerabilities.
Improved Visibility and Control: Companies gain better visibility into their network activities since every access request is authenticated and logged. This centralized monitoring enables early detection of suspicious activity and improves incident response.
Minimizing the Impact of Breaches: In the event of a breach, zero trust limits lateral movement within the network. Even if attackers gain access to one part, they will not easily move between systems, reducing the potential damage.
Regulatory Compliance: Many regulations require companies to implement strict access controls and security measures. Zero trust helps organizations meet these regulatory requirements by enforcing strong identity management and data protection practices.
Better Adaptation to Remote Work: With remote work becoming more prevalent, zero trust allows secure access to company resources from anywhere. It ensures that employees are continuously authenticated, regardless of whether they are on-premises or working remotely.
Scalability and Flexibility: As organizations grow and adopt new technologies, a zero trust strategy allows them to easily scale security controls across new users, devices, and applications without compromising protection.
The primary goal of Zero-Trust is to protect businesses from what is known as "advanced threats" and the effects of data theft.
When cybercriminals steal intellectual property, it leads to lost revenue. When attackers steal sensitive customer data, data breaches and their solutions can result in high costs. In addition, legal disputes, governmental investigations and damage to the company's reputation are often the result.
Zero Trust strategy does not prevent every conceivable attack or breach, but an IT security architecture according to Zero Trust ensures that companies do not fall victim to simple attacks or that these are not discovered for months, perhaps even years. Security experts who are guided by Zero Trust as the main driver of their IT security strategy fulfil many compliance requirements with significantly greater efficiency.
In doing so, a Zero Trust ecosystem should be geared to the business area of every company. Different industries such as eCommerce, energy or finance have different potential entry points for attackers. It is not enough to simply provide technologies. Internal processes, organisational measures and employee awareness of potential risks must also be taken into account.
With the following three steps, we provide you with an initial guide on how to implement Zero Trust and thus comprehensive protection of business-critical data in your own organisation.
Step 1: Assessment
In the first step, it is important to define the organisational framework. To do this, a number of questions must be answered as precisely as possible:
What should be protected and why?
Where are these digital and physical assets located - in the cloud or on local servers?
Which data is classified as public and which is highly sensitive?
Step 2: Discovery & Inventory
Next, all data is visualised in an inventory in order to identify further security-relevant aspects and potential weaknesses. The inventory includes all connected hardware as well as software and operating systems.
Step 3: Preventive measures
The possible measures to eliminate cyber threats from the outset and ensure data integrity are numerous. Some of the most important tools are:
Disk and file & folder encryption
Device control
Application Control with whitelisting
Identity & access management
The complete checklist of the steps you need to take to introduce Zero Trust in your organisation is available for download in our free E-Guide. Order here:
Would you like some basic information about Zero Trust? Then take a look at the recording of our webinar "Never trust, always verify! - the DriveLock Zero Trust platform".
Remote Workforce: Employees working from home or on the go access company resources securely through identity verification and encrypted connections. Regardless of the network they’re on, they are treated as external, and access to corporate data is only granted after continuous checks.
Cloud and SaaS Applications: Zero trust allows companies to secure access to cloud services like Google Workspace, Office 365, or AWS. Each interaction with cloud services is treated with the same scrutiny as if it were on-premises.
Third-Party and Contractor Access: Companies using a zero trust strategy can control and monitor third-party vendors or contractors by limiting their access to only the resources they need and applying the same identity verification and monitoring principles.
Data-Centric Protection: Sensitive data is protected by controlling who can access it, where they can access it from, and what they can do with it. Encryption and access controls ensure that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be easily used.
An employee logs in from a device to access a financial application. Before granting access, the system checks their identity (username/password, MFA), the device’s security posture (e.g., up-to-date software), and location (e.g., known office IP address).
If the verification passes, access is granted only to the financial application, and the employee cannot access other unrelated systems like HR or customer databases. This is based on the least privilege principle.
While the employee uses the system, their behavior is monitored for any unusual activity, such as large data downloads or access requests from different locations in a short time span. Any anomaly triggers alerts or even blocks the session.
A zero trust strategy empowers organizations to defend their critical assets by assuming that no entity, whether inside or outside the network, can be trusted by default. By implementing strict identity verification, least privilege access, and continuous monitoring, businesses can significantly reduce their risk of data breaches and other cyber threats.
As more companies embrace remote work, cloud services, and digital transformation, zero trust is not just a security option but a strategic imperative. It enables organizations to stay agile while protecting their most valuable resources, ensuring that security evolves alongside business needs.
About the author: Andreas Fuchs is a product manager at DriveLock SE and a know-how provider for Zero Trust.

The Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC) is an Australian Government intelligence and security agency who provides advice and assistance on...

Cyber attacks are constantly evolving and becoming ever more sophisticated. It is therefore becoming increasingly important for companies, especially...
The major strategic goal of cyber security in the digital age is to combat and mitigate data breaches. A company's data is its most valuable asset to...